| 熔盐堆超临界二氧化碳布雷顿循环系统与热力学分析 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 卢恒, 赵恒, 戴叶, 陈兴伟, 贾国斌, 邹杨. 熔盐堆超临界二氧化碳布雷顿循环系统与热力学分析[J]. 核动力工程, 2022, 43(2): 32-39. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2022.02.0032 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 卢恒 赵恒 戴叶 陈兴伟 贾国斌 邹杨 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所,上海,201800 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 中国科学院战略性先导科技专项项目(XDA02010000);中国科学院前沿科学重点研究项目(QYZDY-SSW-JSC016);中国科学院上海应用物理研究所育新计划项目(Y955051031);国家重点研发计划(2020YFB1902000) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 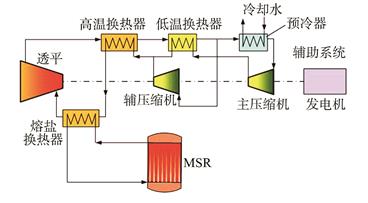
熔盐堆(MSR)能实现在线填料和后处理,出口温度较高,应配备一种与之出口温度相匹配的创新型循环方式,且可达到较高的循环效率。本文基于中国科学院上海应用物理研究所设计的小型模块化熔盐堆(smTMSR-400)设计超临界二氧化碳(SCO2)布雷顿循环系统,使用控制变量法分析了分流比、压缩机/透平效率、主压缩机出口温度、低温换热器换热温差/阻力对SCO2布雷顿循环系统的影响。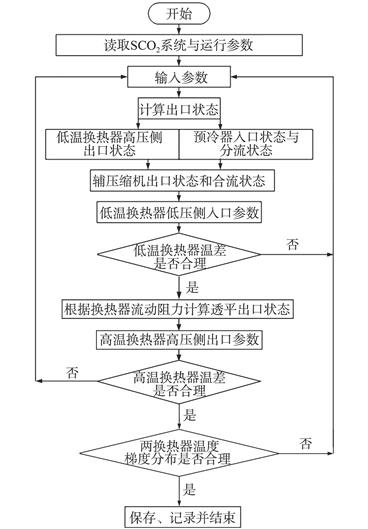
分析结果表明:①存在最佳分流比使低温换热器两侧温差相等;②相较于压缩机效率,等幅度的透平效率提升可使系统循环效率和㶲效率更高;③主压缩机出口压力增大为系统带来正面影响,但循环效率/㶲效率与其斜率都逐渐降低;④换热器换热温差和流动阻力都为系统循环带来了可量化的负担: 换热温差每增加10 K,循环效率降低1.85%,㶲效率降低2.70%;流动阻力每增加1 MPa,循环效率降低6.58%,㶲效率降低10.22%。最后根据分析结果和系统㶲流变化设计了5种物理参考方案。

|
| 关 键 词: | 熔盐堆(MSR) 超临界二氧化碳(SCO2) 布雷顿 热力学分析 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-02-02 |
| 修稿时间: | 2021-10-29 |
|
| 点击此处可从《核动力工程》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《核动力工程》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|




